Acute laminitis cattle affected by acute laminitis generally have a stiff and tender gait an arched back and have the hind limbs and some times thefront limbs also placed well under the body.
Acute laminitis in cattle.
Effects of grain overfeeding and histamine injection on physiological responses related to acute bovine laminitis.
A post mortem x ray study of laminitis in barley beef animals.
Takahashi k young ba.
Antihistamines may be useful e g.
In severe cases cattle may therefore stand cross.
There is some probably unnecessary disagreement over the naming of this condition since there are no laminae on the sole in cattle meaning a more accurate name would be coriitis.
Injectable diphenhydramine 0 5 to 1 0 mg kg iv im.
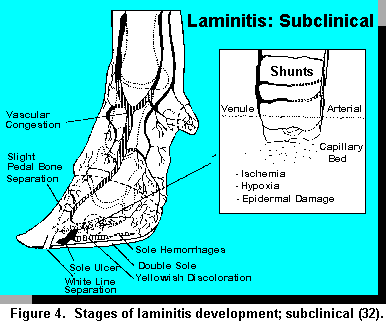
The etiology of subclinical laminitis in cattle is not understood.
Laminitis is more common and more important than it is usually given credit for.
Correct grain overload keeping the animal moving and the claws cool.
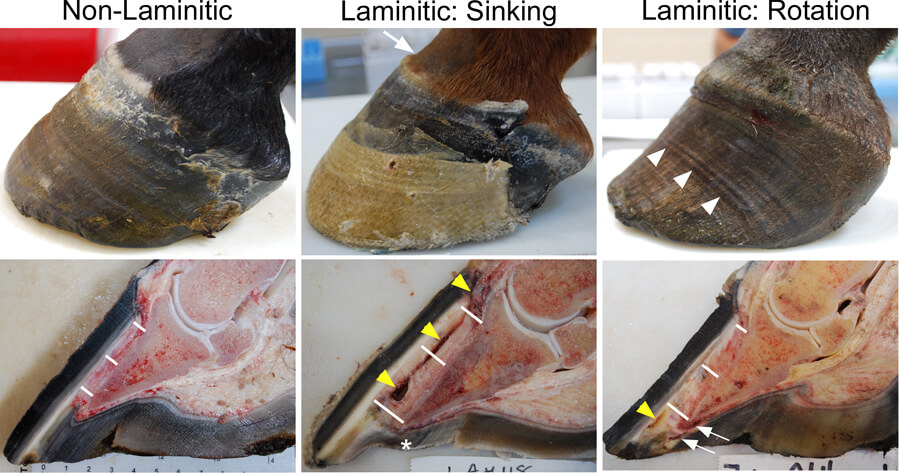
However founder usually refers to a chronic long term condition associated with rotation of the coffin bone whereas acute laminitis refers to symptoms associated with a sudden initial attack including pain and inflammation of the laminae.
Hind lateral and front medial claws are more commonly affected by laminitis than the other claws.
The terms laminitis and founder are used interchangeably.
The classic hypothesis suggests that high levels of carbohydrate in the diet see subacute ruminal acidosis invoke an increase of streptococcus bovis and lactobacillus spp which induce a state of acidosis in the rumen.
Speaking to a large crowd at the national cattlemen s beef association s cattleman s college in denver today tom edwards dvm kearney neb offered some tips on laminitis and responsible handling of downed cattle.
This causes gram negative organisms to die and release vasoactive endotoxins.
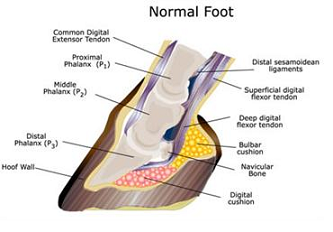
Inflammation of the sensitive corium causes pressure pain and loss of cohesion between the horn and the underlying structures of.